Strokes are medical emergencies that can affect a wide range of individuals. They are both cardiovascular and neurological diseases since they directly affect the blood vessels in and leading to the brain. Having a stroke is among the top 5 leading causes of death in the US.
What Causes a Stroke?
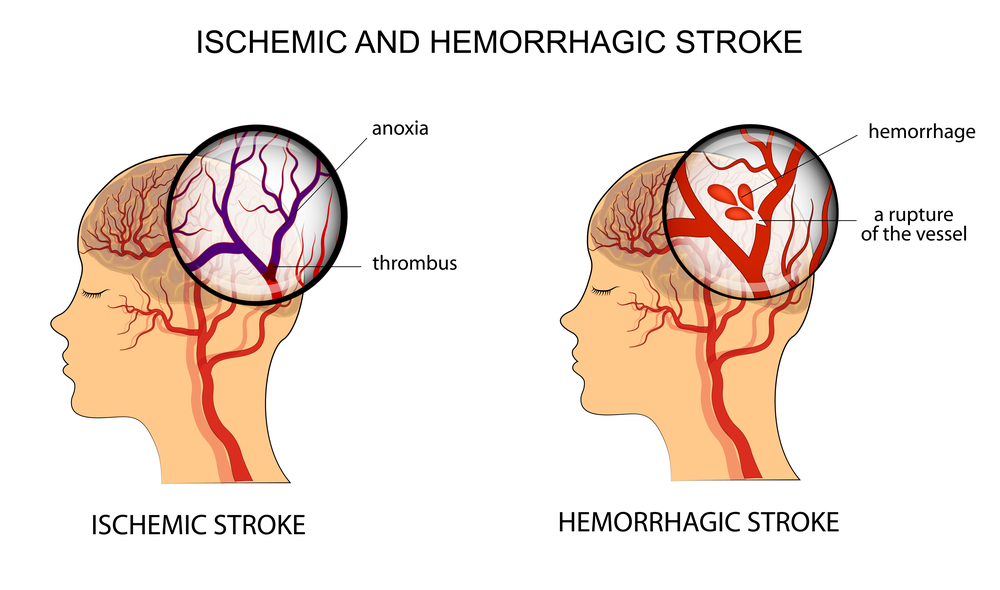 For the brain to function thoroughly, it needs a constant supply of oxygen carried by the blood supply. A stroke is brought on by an interruption in the blood supply to the brain. The sudden lack of nutrients and oxygen being provided to the brain can cause neurological complications as brain cells die off rapidly.
For the brain to function thoroughly, it needs a constant supply of oxygen carried by the blood supply. A stroke is brought on by an interruption in the blood supply to the brain. The sudden lack of nutrients and oxygen being provided to the brain can cause neurological complications as brain cells die off rapidly.
There are two types of strokes:
- Ischemic stroke: caused by a blood clot or other obstruction in the blood vessels
- Hemorrhagic stroke: caused by a ruptured blood vessel
When either of these strokes occurs, it creates issues with the brain’s ability to provide functionality to parts of the body.
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) causes a temporarily decreased amount of blood supply to the brain but doesn’t cause permanent damage the way the other two types of strokes do.
What are the Signs of a Stroke?
The best and most effective treatment options available for stroke victims depend on how quickly the stroke is spotted. There can be a decreased chance of brain injury if symptoms are caught immediately. These include:
- Sudden confusion characterized by trouble speaking or understanding speech
- Sudden weakness or numbness in the left arm, face, or leg
- Trouble seeing out of one or both eyes due to blurred or blackened vision
- Rapid loss of coordination brought on by dizziness.
Strokes can happen in different areas of the brain, causing different types of symptoms and side effects. For example, if the blood vessels in the occipital part of the brain are affected, the victim will experience changes in their vision. Affected vessels in the frontal lobe will cause emotional and speech complications.
After a stroke, some permanent disabilities can occur. These include paralysis, memory loss, changes in behavior and emotions, and difficulty thinking, swallowing, talking, or moving certain muscles.
Who is at Risk of Having a Stroke?
There are a few notable and preventable risk factors for a stroke, including lifestyle choices like heavy drinking, cigarette smoking, obesity, and drug use. These lead to more serious risk factors, including:
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- High blood pressure
Men have a higher risk of having a stroke than women, especially those who are 55 years of age or older. Birth control or hormonal medication increases the risk of stroke as well.
Conclusion
Strokes require immediate attention and care. Those who experience TIAs are likely to experience a major stroke within a year, especially if care isn’t taken to prevent further neurological disruptions. All strokes can cause either permanent or temporary neurological complications.
Prevention can be as simple as getting better exercise, eating a proper low-cholesterol diet, managing diabetes, avoiding illegal drugs, and quitting excessive alcohol and tobacco use.



